Ovarian cancer is often called the “silent killer” because it may progress without noticeable symptoms until advanced stages. Early detection is crucial for improving survival rates and achieving effective treatment.
Dr. Shweta Mendiratta, a top gynecologist in Faridabad, emphasizes that awareness, timely checkups, and understanding risk factors can make a significant difference in women’s health outcomes.
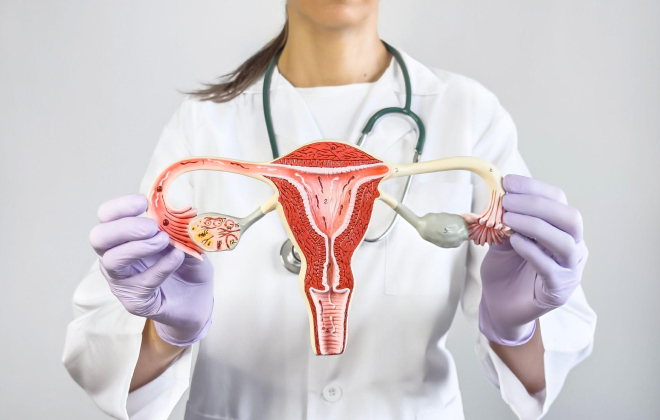
What is Ovarian Cancer?
Ovarian cancer originates in the ovaries, the reproductive organs responsible for producing eggs and hormones such as estrogen and progesterone. There are several types, including:
- Epithelial Ovarian Cancer: Most common type, starting in the cells lining the ovary.
- Germ Cell Tumors: Develop from egg-producing cells, often in younger women.
- Stromal Tumors: Rare tumors from hormone-producing cells.
Why Awareness Matters
Ovarian cancer is often diagnosed late due to vague or mild symptoms. Raising awareness helps women recognize early warning signs, undergo timely screenings, and consult a gynecologist for proper evaluation.
Early detection can:
- Improve treatment outcomes
- Increase survival rates
- Allow less aggressive surgical procedures
- Preserve fertility in some cases
Common Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer
While early-stage ovarian cancer may not cause noticeable symptoms, common warning signs include:
- Persistent bloating or abdominal swelling
- Pelvic or abdominal pain
- Difficulty eating or feeling full quickly
- Urinary urgency or frequency
- Unexplained fatigue
- Changes in bowel habits
- Unexplained weight loss or gain
- Menstrual irregularities
Dr. Shweta Mendiratta stresses that noticing these subtle changes and reporting them to a gynecologist promptly is key to early diagnosis.
Risk Factors for Ovarian Cancer
Certain factors increase the likelihood of developing ovarian cancer:
- Age: Risk increases after age 50, but younger women can also be affected.
- Family History: Mutations in BRCA1 or BRCA2 genes and a family history of ovarian or breast cancer.
- Reproductive History: Women who have never been pregnant have a higher risk.
- Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT): Long-term HRT may increase risk.
- Lifestyle Factors: Obesity, smoking, and diet may contribute to risk.
Screening and Early Detection
There is no universal screening for ovarian cancer, but certain tests can help detect it early in high-risk women:
- Pelvic Examination: A routine gynecological exam can detect abnormalities in the ovaries.
- Ultrasound (Transvaginal Ultrasound): Helps visualize ovarian cysts or tumors.
- CA-125 Blood Test: Measures a protein often elevated in ovarian cancer.
- Genetic Testing: Women with a strong family history may benefit from BRCA mutation screening.
Early consultation with a gynecologist ensures timely evaluation and monitoring.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the type, stage, and overall health of the patient:
- Surgery: Removal of the tumor, affected ovary, or uterus depending on the spread. Robotic-assisted surgery is increasingly used for precision and faster recovery.
- Chemotherapy: Often administered after surgery to eliminate remaining cancer cells.
- Targeted Therapy: Drugs designed to attack specific cancer cells while sparing healthy tissue.
- Radiation Therapy: Rarely used, but may be recommended in specific cases.
Dr. Shweta Mendiratta, a specialist in gynecological oncology, combines advanced surgical techniques with personalized treatment plans to optimize patient outcomes.
Prevention Tips
While ovarian cancer cannot always be prevented, certain measures reduce risk:
- Regular Gynecological Checkups: Early evaluation for high-risk women.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Balanced diet, regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight.
- Family Planning Considerations: Pregnancy and breastfeeding may reduce risk.
- Genetic Counseling: For women with family history or BRCA mutations.
- Awareness of Symptoms: Early reporting of abdominal or pelvic changes.
FAQs: Ovarian Cancer Awareness
- Can it be detected early?
Yes, early detection is possible through regular gynecological exams, ultrasound, and blood tests for high-risk women.
- What are the early warning signs?
Bloating, pelvic pain, urinary changes, early satiety, fatigue, and menstrual irregularities may indicate early ovarian cancer.
- Who is at high risk?
Women with family history, BRCA gene mutations, older age, never being pregnant, or long-term hormone therapy are at higher risk.
- Is it hereditary?
Yes, mutations in BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes significantly increase the risk, making genetic counseling important.
- Can robotic surgery treat ovarian cancer?
Yes, robotic-assisted surgery allows precise tumor removal, smaller incisions, and faster recovery for suitable candidates.
- How often should I get checked if I’m high risk?
High-risk women should consult their gynecologist for personalized screening schedules, which may include annual ultrasounds and CA-125 tests.
- Can OV be cured if detected early?
Early-stage OV has a high chance of successful treatment, often involving surgery and chemotherapy.
Conclusion
Ovarian cancer awareness and early detection save lives. Women should stay vigilant, recognize warning signs, and consult a gynecologist for timely evaluation.
Dr. Shweta Mendiratta, a top gynecologist in Faridabad, advocates preventive care, regular screenings, and advanced treatment options like robotic surgery. Her expertise ensures that women receive compassionate, effective care tailored to their needs.
Prioritize your health, stay informed about early symptoms, and schedule regular gynecological checkups — early action can be life-saving.